Managing users
There are two main ways to manage user records in the system: "Internal user management" and "Integration with a directory service". See a brief explanation on each of these modes
Internal user management
Records are managed by the system, including access credentials. It is possible to configure the security level of passwords, such as minimum length, validity, and blocking rules. There are four ways of managing users internally:
- Internal record: Users can be manually registered in the system, with a login and password for authentication.
- Integration via web service: Authenticated web services allow for adding or editing users through other services.
- Import via database: Data can be inserted directly into the system's database, for subsequent user import.
- Import via XLS file: It is possible to provide a spreadsheet with user data for manual or scheduled import.
For more details on these forms of management, refer to the Integration guide.
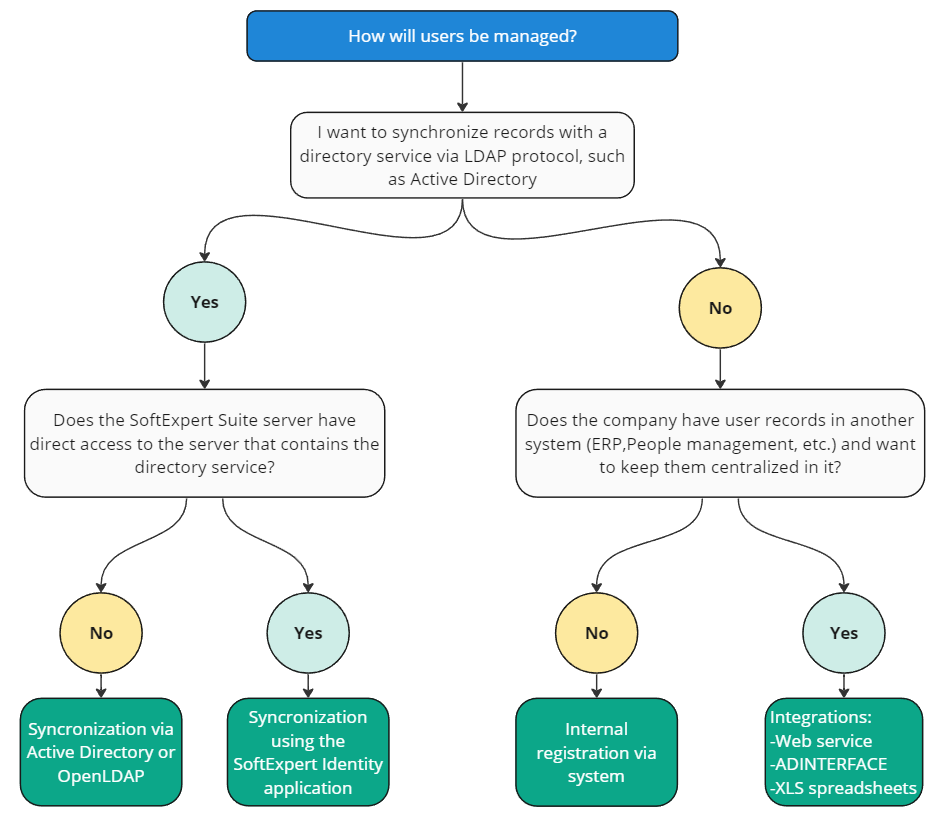
Integration with directory service via LDAP protocol
The system allows for synchronizing users with a directory service, such as Microsoft Active Directory or OpenLDAP. An external authentication server manages user credentials. Communication with the directory service may be established in two ways
- Direct communication: If the system's server is in the same domain, or the service is accessible externally, synchronization can be done via the LDAP protocol.
- SoftExpert Identity application: Recommended for customers hosted on cloud servers, this application works as an intermediary, transferring user data to the system.
Use the flowchart made available to help you choose the best way to manage users.
Attention:
- It is possible to have users synchronized with directory service combined with non-synchronized users. However, only non-synchronized ones can use the internal authentication mode.
- Direct synchronization with the directory service and the SoftExpert Identity application cannot be used together. You must choose one method only.
User expiration New
In version 2.2.3, the access expiration feature was introduced to allow
administrators to set an automatic expiration date for both internal and
external users.
With this resource, a daily verification process will automatically deactivate those users whose expiration dates have been reached. This simplifies the management of temporary accesses and increases security by cancelling unnecessary or old accesses.
This update makes for an easier user management, ensuring that only active and authorized accounts keep accessing the system, which is ideal for companies dealing with accesses that are temporary or valid for a given amount of time.
How to insert a user expiration date?
Prerequisites:
Access to the Administration > File >
Organizational unit: User (AD004) menu
Access to the
Administration > File > External user (AD060) menu
In the records of both internal and external users, a field called Expiration date has been added. Insert a date, starting from the current date, to define when the user's access must be canceled automatically.
- Internal users cannot set an expiration date for their own account.
- External users can view their expiration dates from the Account menu, but will not have permission to edit them.
When is the User expiration routine executed?
The user deactivation routine is executed daily through the
InactivateExpiredUsersJob job, which automatically deactivates all accounts
whose expiration dates have been reached, ensuring an efficient and secure
access control.